Aurora Forecast: See The Northern Lights Tonight & Tomorrow!
Ever gazed upon the shimmering curtains of light dancing across the night sky? The aurora borealis, or northern lights, and its southern counterpart, the aurora australis, are a mesmerizing spectacle driven by the dynamic weather occurring far beyond our planet.
The allure of the aurora has captivated humanity for centuries, inspiring awe and wonder. But what exactly causes these celestial displays, and how can you predict where and when they might grace your skies? The answer lies in understanding space weather and the tools scientists use to forecast these dazzling events. This article delves into the science behind the aurora, the forecasting methods employed, and how you can plan your own aurora-viewing adventure.
The foundation of understanding the aurora is grasping that space, too, experiences "weather." While not involving rain or snow, this space weather consists of solar winds and magnetic waves coursing through the vast expanse. These phenomena, originating from the sun, interact with the Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere, creating the conditions for the aurora. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) plays a crucial role in monitoring and forecasting these space weather events.
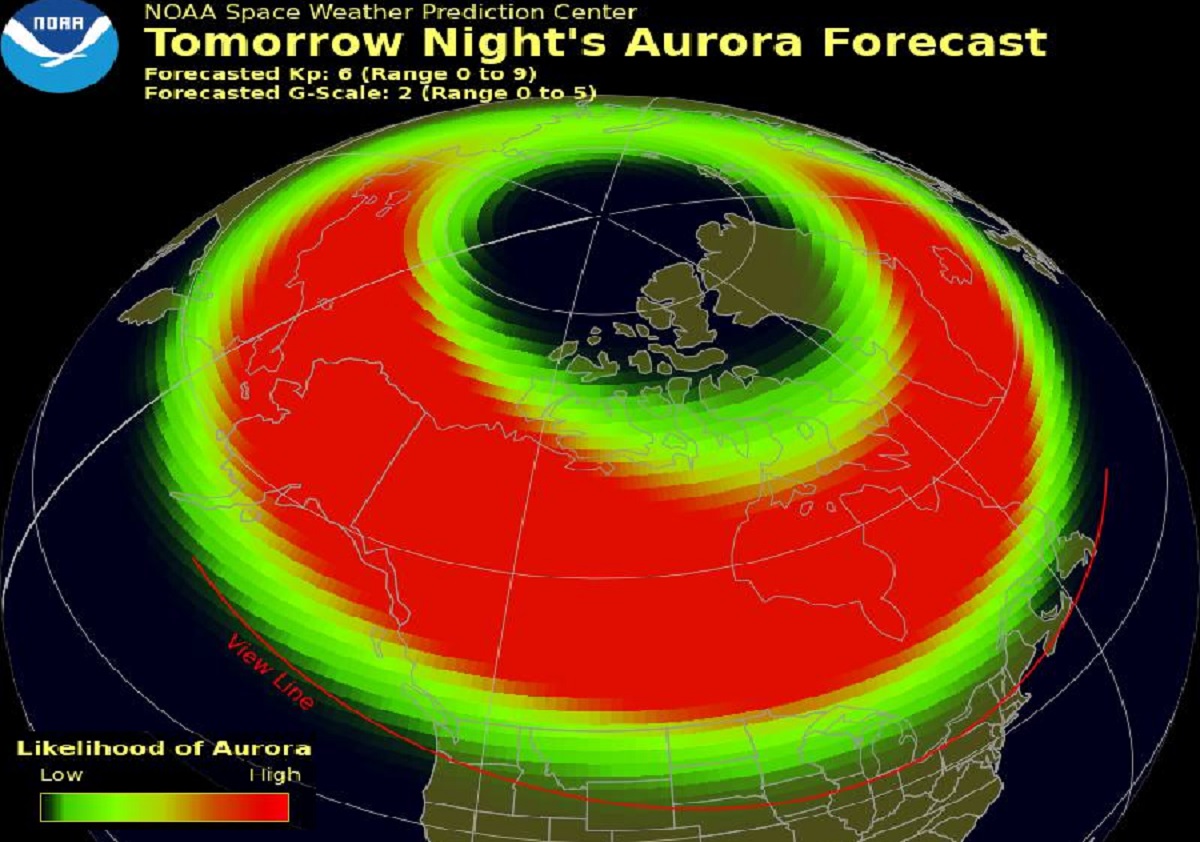
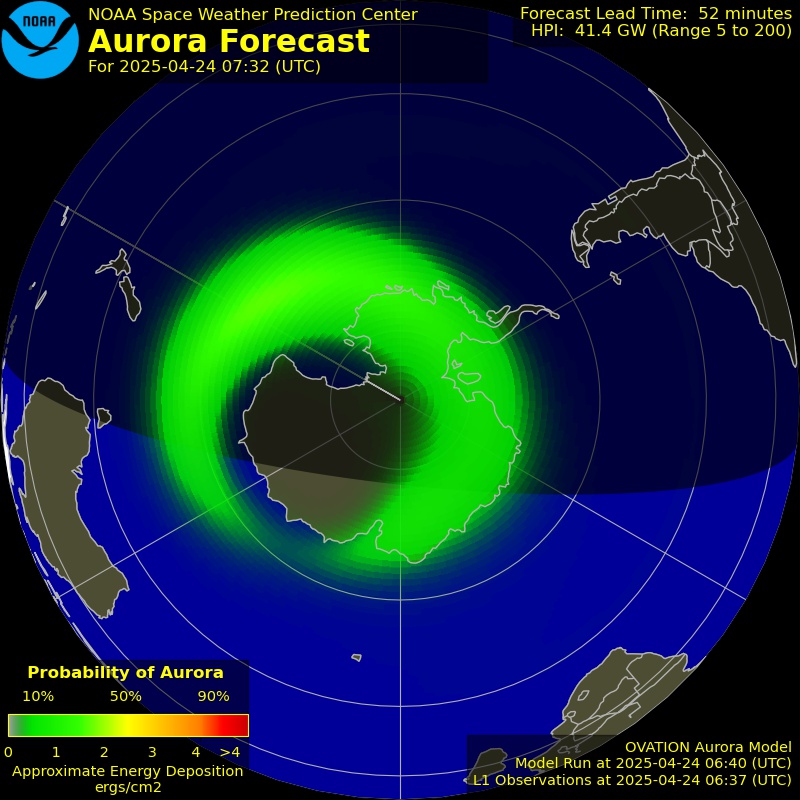
The core of the aurora forecast relies on several key elements. The "ovation model," a sophisticated tool, provides a 30 to 90-minute forecast of the aurora's location and intensity. This model utilizes data from various sources, including observations from the L1 observation point, a location in space where solar wind activity is constantly monitored. The forecast lead time the time it takes for the solar wind to travel from the L1 observation point to Earth is a critical factor in accurate predictions. This allows scientists to predict the visibility and location of the auroras based on factors like geomagnetic activity, solar radiation, and radio blackout events. The forecast encompasses the northern and southern lights, providing a comprehensive view of potential auroral displays across both hemispheres.
Several resources are available for aurora enthusiasts. Charts, animations, and forecasts for the next three days provide a detailed outlook. Viewline maps offer specific predictions for tonight and tomorrow night, guiding viewers to the best locations. Additional resources teach the science and offer tips for aurora viewing. Understanding the alerts, watches, and warnings issued by NOAA is critical. These indicate the level of geomagnetic activity and the likelihood of auroral displays. For instance, the bottom half of specific charts is frequently used to identify the areas where auroras are most likely to be visible. The aurora forecast is an hourly tool and an indicator for planning viewing opportunities.
Inside the auroral oval, where the aurora is most frequently observed, the KP index, a measure of global geomagnetic activity, is less critical. Even when global activity is low, the area can still host high auroral activity. This is important to consider when interpreting forecasts. Some instances, like the aurora viewing forecast for April 15, 2025, provide specific dates for planning viewing. In addition, the NOAA SWPC offers updates on the forecast, such as that geomagnetic storm conditions are expected to increase.
Improvements in forecasting methods have been ongoing. On October 26, 2020, the Space Weather Prediction Center announced the operational release of improved 30-minute auroral prediction maps. The space weather prediction center's website is a valuable resource, providing the latest forecasts and outlooks. These improvements enable more precise and timely forecasts, increasing the chances of witnessing the aurora. The site provides forecasts for both the northern and southern hemispheres. When and where the aurora can be seen will depend on space weather activity and will be clearly detailed in the charts. In addition, the animations that show the movement of the aurora over the past 24 hours and offer predictions for the next half hour, provide an additional value. The vibrant colors of the aurora provide an astonishing display.
The reports and forecasts of solar and geophysical activity, along with predictions of sunspot numbers and radio flux, provide insights into the underlying conditions that influence auroral displays. The AP index, a measure of geomagnetic activity, is another useful indicator, especially during peak auroral events. For example, the AP index was reported on June 15, 2024, at 2205 UTC. Another useful tool for aurora enthusiasts is the NOAA aurora forecast channel. This visualization provides an overview of the probability of aurora and its intensity.
Auroral enthusiasts also know that the appearance and the color are important in the viewing experience. Typically, the calculated aurora oval has green colors. But sometimes the middle part turns yellow or red. The characteristics of the aurora include the ability to show if auroras are tame or wild, which is very important for viewers. The negative number that you are looking for will always be a good indicator. The aurora can be observed even farther from the poles during large events.
Planning an aurora-viewing experience requires several considerations. The skies must be clear and free of clouds. Also, darkness is essential. This will prevent the summer months from preventing auroral viewing, and in the northern and southern latitudes, the midnight sun is an issue. The ovation aurora forecast model provides the intensity and location predicted at the top of the map. A daily deterministic and probabilistic forecast is available for geomagnetic activity. In addition, the northern lights will be visible over portions of the northern U.S., according to the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center's aurora forecast. Moreover, the aurora will be visible over much of Canada.
The ability to accurately predict the aurora is constantly improving, thanks to ongoing research and technological advancements. The use of real-time data, sophisticated modeling, and continuous monitoring of space weather events enhances the accuracy of forecasts. Furthermore, the information is available at various user levels, so even beginners can understand and appreciate this magnificent natural phenomenon.